
Bible: Hebrew, Exodus 7:3. This development occurs in approximately 2 to 9 days, depending on temperature and humidity.Famous quotes containing the words signs and, signs and/or symptoms: But I will harden Pharaoh’s heart, and I will multiply my signs and wonders in the land of Egypt. These tiny (about a centimetre long) thread-like Adult hookworms live in the small intestine and shed eggs in feces and into the environment, where they larvate, hatch, and develop into infective third-stage larvae. Merely walking barefoot on the ground containing hookworm-infested feline stool can trigger an infection. Humans can be infected by hookworms even without ingestion.
Sings And Symptoms Of Hookworms In Humans Skin For Very
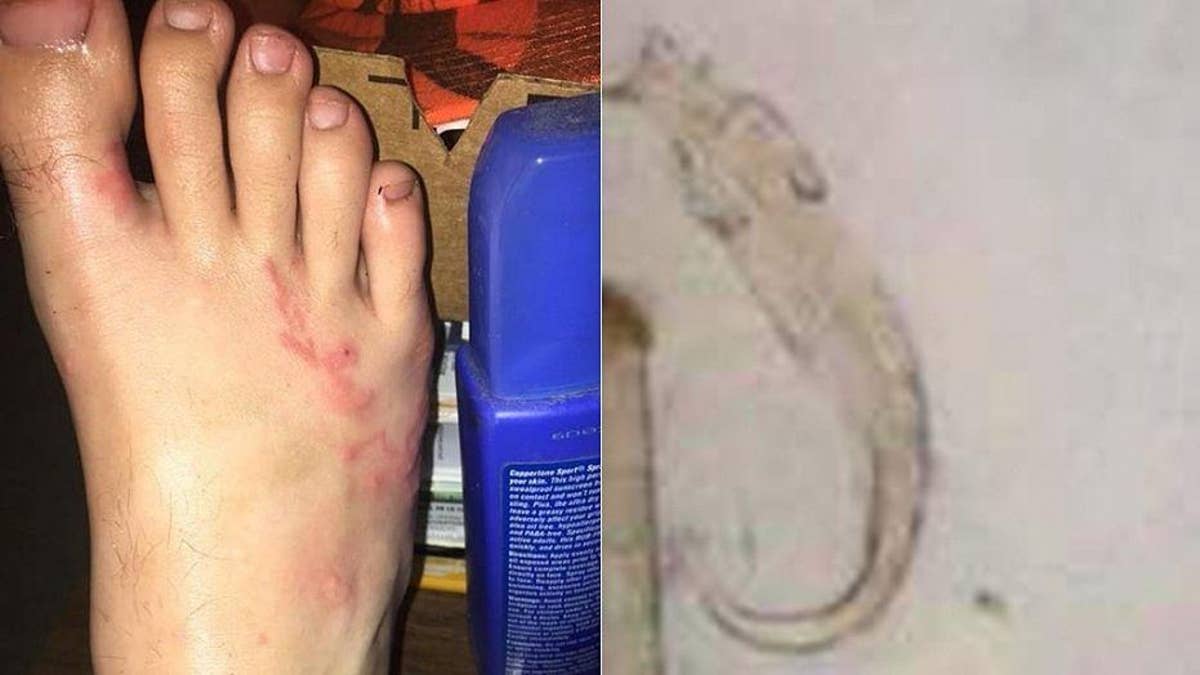
Arrested development may also occur in the mucosa of the small intestine. Caninum will migrate through the lungs and enter somatic tissue, where the larvae become dormant, or arrested. In dogs more than 3 months of age, some A. Dogs may also become infected by eating cockroaches that contain infective larvae.Transmammary transmission of larvae from the bitch to pups is an important route of infection for A. Because the hookworm cant survive in human skin for very long.Dogs become infected with hookworms via ingestion of the third-stage larvae from a contaminated environment, larval penetration of the skin, and/or ingestion of other vertebrate hosts with infective larvae in their tissues. 1933)Creeping eruption causes severe itching, blisters, and a red growing, winding rash.
Small bleeding ulcers form where the worms once fed.Adult worms may live for 4 to 24 months in the small intestine. Worms may detach and move to new sites and reattach. When a dog ingests these larvae in animal tissues, the larvae travel to the small intestine, where they are released and mature into adult worms.Immature and adult worms attach to the mucosa of the small intestine, digest the tissue, inject anticoagulants, and suck blood.
Caninum is most severe in young pups that are infected through nursing (the transmammary route) shortly after birth. Disease in dogs caused by infection with A. Caninum is a voracious bloodsucker and can actually bleed a puppy to death.

Braziliense because they are voracious bloodsuckers and consume much more blood than the latter. Ancylostoma caninum is more pathogenic than A. Respiratory signs may also be associated with hookworm-induced anemia. Respiratory disease and pneumonia may occur in puppies when large numbers of larvae migrate through the lungs.
Braziliense are most often the culprits Ancylostoma caninum and A. These lesions are most commonly seen on the animal's feet, particularly in the interdigital spaces.
The geographic distributions of A. Ancylostoma prevalence ranged from less than 5% in the west to 36% in the southeastern United States. Eggs and 1.02% contained Uncinaria spp. In a survey conducted in 1996 using fecal samples collected from dogs across the United States, 19% of the fecal samples contained Ancylostoma spp. Both young and adult canine and feline hosts can harbor hookworms and pass eggs in their feces.
Puppies should be routinely dewormed for hookworms. Because somatic infection is common in adult dogs (even those on routine monthly intestinal parasite control), veterinarians should assume that essentially every nursing pup is at risk for hookworm anemia. Caninum larvae from mother to nursing offspring contributes to the high prevalence of infection in puppies, even in pets that are well cared for and routinely treated for intestinal parasites. Uncinaria stenocephala, or the northern carnivore hookworm, prefers colder climates and is most common in the northern United States, Canada, and Europe. Braziliense occurs in warm coastal areas however, this parasite is most common in tropical and subtropical regions of Central and South America and the Caribbean. In the United States, A.
In general, the environmental stages thrive best away from direct sunlight in warm, moderately moist, aerated soils. Most hookworm eggs larvate, hatch, and develop into infective third-stage larvae in the environment in approximately 2 to 9 days, depending on temperature and humidity. Tubaeforme and 13 to 27 days for A. Similar variations are seen in other hookworm species, but in general, the prepatent periods are 18 to 28 days for A. Ancylostoma caninum usually becomes patent in 2 to 3 weeks, but puppies infected while nursing may shed eggs as early as 10 to 12 days after birth. Infection with hookworms occurs in all dogs, but infection rates are likely to be higher in pets kept outdoors.Click here to view our Prevalence Maps and to sign up for updates on reported cases in your areaPrepatent Period and Environmental Factors



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
